HIV/AIDS
Table of Contents
- What is HIV?
- How many people are affected?
- How Is It Acquired or Transmitted?
- What Are the Signs and Symptoms of HIV/AIDS in Men and Women?
- What are the effects of HIV infection?
- Causes and Risk Factors
- How can HIV infections progress?
- Complications of HIV/AIDS: Categories, Examples, and Treatment
- How is HIV infection diagnosed?
- The Ultimate Guide To Treatment of HIV/AIDS
- What Is AIDS and How Is It Related to HIV?
- What Are The Treatment Options for AIDS?
- 10 Essential Methods of Prevention and Spread of HIV/AIDS
-
Frequently Asked Questions About HIV/AIDS
- 1. What are the top 3 risks for acquiring HIV?
- 2. How accurate are HIV tests?
- 3. What is the life expectancy of someone who has HIV?
- 4. What is the life expectancy of someone who has AIDS?
- 5. How will HIV affect my child If I get pregnant?
- 6. Can I still engage in sexual activities even if I am diagnosed with HIV?
- 7. When should I seek for an HIV Test?
- 8. How long does HIV progress to AIDS?
- 9. What should I expect if I have HIV/AIDS?
- 10. Are there any foods to be avoided if diagnosed with HIV?
- 11. How frequently should I visit the doctor if I have HIV?
- 12. Can HIV be transmitted through other modes other than bodily fluids?
- 13. Is there any chance that I can be cured with HIV or AIDS?
- 14. How does age affect the possibility of acquiring HIV?
- 15. How does smoking increase the risk of HIV?
- 16. I’ve been diagnosed with HIV and I have undergone treatment. My latest HIV screening says that there is no virus detected in my body. What does this mean?
- 17. What happens if I miss my treatment or discontinue my treatment?
- 18. Can you stop taking HIV treatment?
- 19. What are the top three countries with the highest HIV-positive population?
- 20. Is there a population that is HIV-resistant?
- 21. What does the term safer sex mean?
- 22. Are condoms truly effective in the prevention of HIV transmission?
- 23. How do I make the best choice of condoms to use?
- 24. Is it okay to use lubricant together with a condom?
- 25. What is post exposure prophylactic treatment?
- 26. In what ways can injecting drug users lower their risk of getting HIV?
- 27. Can mother to child transmission (MTCT) be prevented? How?
- 28. What are universal precautions?
- 29. What is the mechanism of action of antiretroviral drugs?
- 30. Are antiretroviral drugs efficacious?
- References
What is HIV?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus is a virus that affects and damages a person’s own immune system - the same immune system that fights off common infections If left untreated, this virus can progress up to 15 years and eventually damage T Cells, which are a type of immune cells making the people affected by it vulnerable to even common illnesses and even cancer.
Scientists have identified a type of Central African chimp as the original carrier, and source, of the HIV virus. They believe the chimpanzee version, a 32,000-year-old retrovirus called simian immunodeficiency virus, was probably transmitted to humans before mutating to become HIV back when the chimps were hunted for their meat.
Though it wasn’t discovered until the 1980’s, scientists firmly believe the virus has existed in the US since the mid to late 1970’s, and it could have jumped from chimps to humans back in the late 1800’s.
The AIDS virus was first discovered in 1983, although scientists called it by another name then - human T-cell lymphotropic virus-type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Today, scientists believe humans could have carried this mysterious virus as far back as the late 1800’s. During the mid-80’s and early 90’s, treatment for HIV was becoming more mainstream, and went through many adjustments. When patients contracted AIDS, they were often admitted to AIDS wards in hospitals for the sole purpose of end-of-life care.
In 1984, ‘AIDS Action’, a community-based organization, was already meeting in Washington DC to protest what has quickly become a national epidemic. Thankfully, the worst days of the disease are long behind us. Unlike 30 or 40 years ago, there is no reason patients can live the same fulfilling life they had before the virus, as long as they seek treatment and adhere to it!
How many people are affected?
That the first AIDS cases occurred in the USA and that the HI virus was discovered almost simultaneously by two research groups was only a little more than 30 years ago. Since then, HIV infection has developed into a disease that spans countries and continents and is one of the greatest medical problems of our time.
According to UNAIDS (United Nations Joint Programme to Reduce HIV/AIDS), at least 36.9 million people worldwide were infected with HIV in 2017, including 1.8 million children under 15. In Europe, 397 new HIV-positive diagnoses were registered in 2018. This figure is similar to that of recent years. This means that at least one person is infected with HIV every day.
How Is It Acquired or Transmitted?
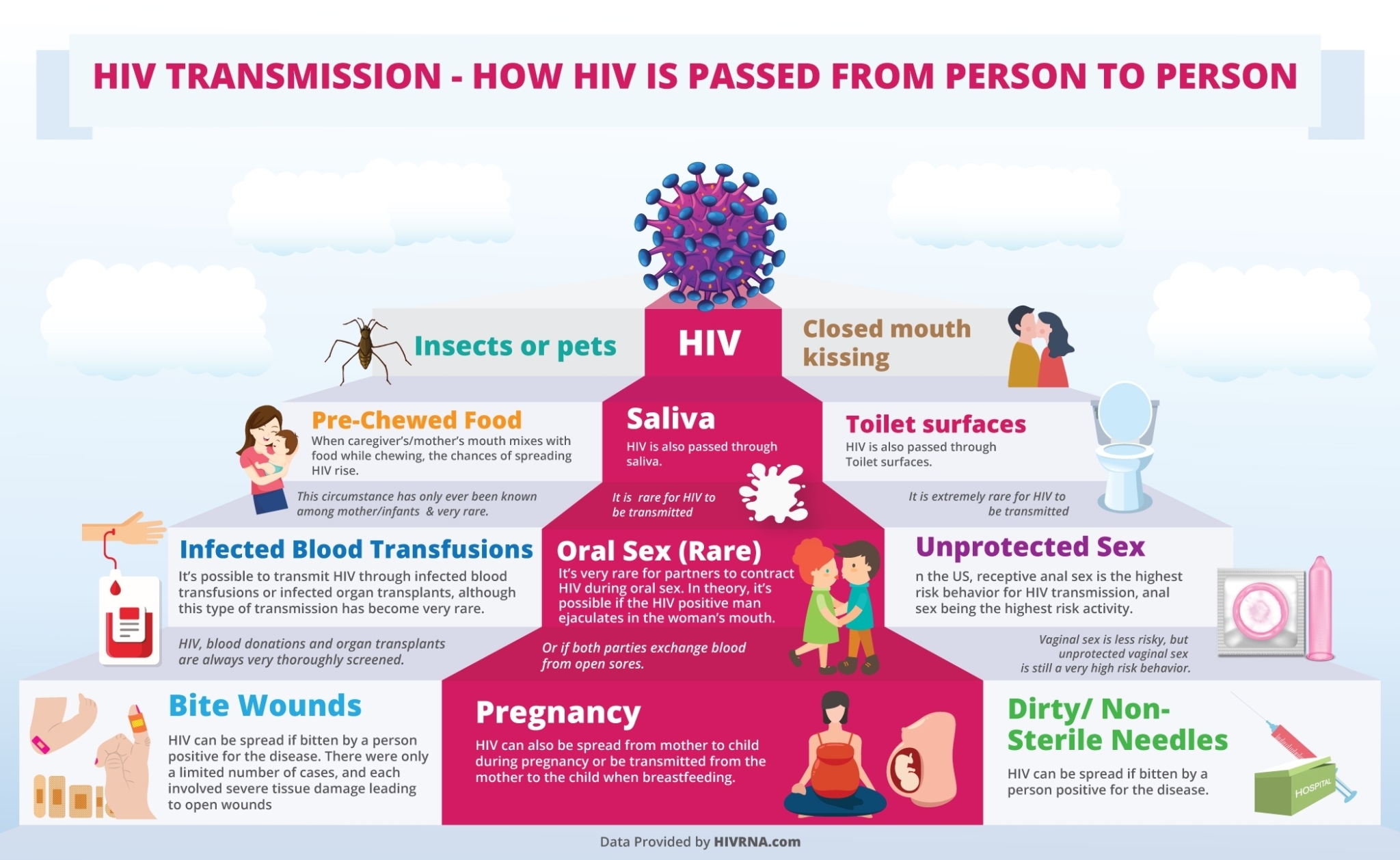
HIV is identified as one of the prevalent sexually transmitted diseases around the world. It can be transferred from human to human, mostly through the following:
- Bodily fluids. Bodily fluids such as blood, semen, breastmilk (for mother to child transmission) and vaginal or rectal fluids.
There are many ways as to how body fluids can be transferred, some of these ways are the following:
- Sharing of needle/tattoo equipment. For people who are sharing needles for drug use, blood transfusion or tattoo equipment, the virus can be transmitted through the needles.
- Blood Transfusion. If a person infected with HIV donates blood to another person, it is likely that HIV will also be transmitted - this is why screening of blood donors is very important.
- Vaginal, Anal or Oral Sex. Body fluids such as semen, vaginal fluid can be transferred to another person if they are engaging in sexual activities. Even for those who are engaging in oral sex only, the fluids carrying the virus can be transmitted to another, especially if they have open wounds in their mouth. Acquiring HIV through sexual activity is also more prevalent in men having intercourse with other men.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of HIV/AIDS in Men and Women?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is one of the worlds’ common sexually transmitted diseases. This is prevalent in most people who are engaged in sexual activities such as oral, anal and vaginal sex and have multiple sexual partners.
Some people who acquire this disease may not be aware that they have the disease as it can be asymptomatic or the symptoms may appear at a later stage of the disease. Below are some helpful questions and their answers if you’re looking to check the symptoms of someone who is possibly HIV-positive.
When Do Symptoms Occur?
Around 65% of the people who have been diagnosed with HIV experience symptoms two to four weeks after contracting the virus. Commonly, these symptoms are similar to symptoms of flu and occur within days up to weeks. Most HIV-positive people recover from such symptoms. The remaining 35% of the people with HIV do not have any symptoms or observations experienced as this time it is still an early stage of HIV.
If you have multiple partners or you have risks of acquiring HIV, it is better to get tested.
What Are The Different Symptoms in Stages of HIV?
There are three major stages of HIV that are recognized. These are as follows:
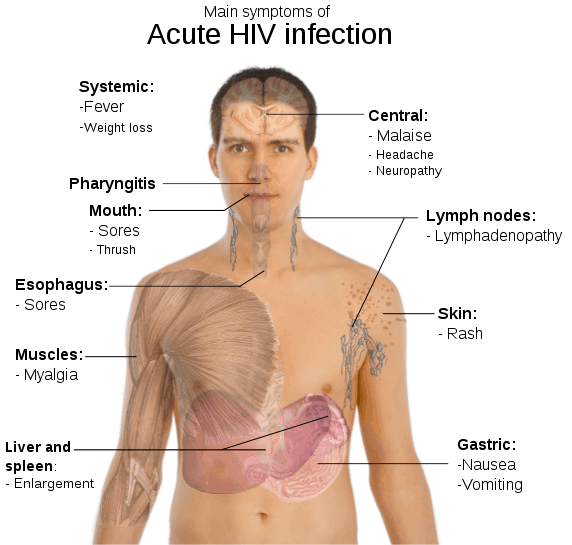
Acute HIV Infection
This is the stage where the first flu-like symptoms appear and happens usually within two to four weeks after being exposed to the virus. Not all HIV-positive people experience symptoms but those who do experience the following:
- Fever
- Nausea
- Sore Throat
- Swollen Lymph Nodes
- Muscle Aches
- Fatigue
- Appetite Loss
- Night Sweats
- Rashes
- Ulcers in Mouth and Genital Area
- Headache
A person with HIV may experience one or a few of the symptoms and those symptoms may appear within days or weeks after experiencing it.
Chronic HIV Infection
This stage occurs after the Acute HIV Infection and before the onset of the AIDS stage. The symptoms that occur in this stage are more evident and severe and evident. These symptoms include:
- Difficulties in Breathing
- Excessive Coughing
- Rapid Weight Loss
- Diarrhea
- Excessive Fatigue
- High Fever
However, some people may still experience no symptoms at this stage - this is when HIV presents itself as a latent infection and this stage can last up to a decade.
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
This is the final stage of HIV and the person has CD4 levels below 200 cells per cubic millimeter. By this stage, the symptoms are severe and can interfere with daily life. The symptoms will be listed in the question below.
What Are The Severe Symptoms of AIDS?
- Severe Chills
- Persistent High Fevers (over 37.8°C)
- Weight Loss
- Persistent Headaches
- Problems in Memory
- Rashes
- Severe Fatigue
- White Spots in Mouth
What Are The Common Symptoms for Men?
Symptoms may occur to both men and women but studies show that vague symptoms may appear on men than women. These symptoms are unspecific and are just bearable which is why they are usually mistaken as flu or another condition. Here are some of the symptoms that most men who have HIV experienced:
- Fever
- Skin Rashes
- Sore Throat
- Unexplained Tiredness
- Dementia
- Weight Loss
- Ulcers in the mouth or Genital Area
- Night Sweating
- Fatigue
- Muscle and Joint pain
- Swollen Lymph Glands
- Night Sweating
Most men who have multiple partners and are engaging in sexual activities with other men are at high-risk so if you have any experience with the symptoms above, it is highly recommended to get tested.
What Are The Common Symptoms for Women?
While most symptoms experienced by men can be experienced by both men and women, there are some symptoms that are more evident in women. Such symptoms include:
- Changes in Menstrual Period. Women who have acquired HIV may experience in a change in the number of days per cycle, the heaviness of the period or the complete stop of their period. The premenstrual symptoms may also become sever once they have HIV.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. Some women who have acquired HIV may develop PID which causes infection in the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
- Increased Occurrence of Other Sexually Transmitted Infections. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) - the virus which causes genital warts, and genital herpes are some of the sexually transmitted infections that are more apparent in people who are HIV-positive.

Get tested for HIV
STD testing is the only way to know for sure if you do or do not have an STD. Act immediately and get tested today!
Get tested for HIV todayWhat are the effects of HIV infection?
The HIV virus belongs to the so-called retroviruses. In order to multiply, this virus type integrates its genetic material into that of the host cell. The host cell is reprogrammed in such a way that it produces the components for new virus particles itself. The HI virus attacks T-helper cells, in particular CD4 lymphocytes or CD4 cells.
CD4 lymphocytes are white blood cells (leukocytes) and play a crucial role in the coordination of immune defense. The HI virus directly destroys a certain proportion of T-helper cells and also impairs their functions. The less functional CD4 cells are found in the blood, the more severely the immune system is affected.
As the disease progresses, the number and functionality of the helper cells decrease, resulting in the immune system's inability to protect the organism from disease. As a result, the patient's health deteriorates dramatically and, in the absence of treatment, he or she dies.
Causes and Risk Factors
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a lentivirus that causes damage and failure of the immune system. HIV is characterized by the virus killing CD4 Cells. CD4 cells are a type of immune cells called T-Cells. Over a period of time, these CD4 cells are killed by the virus and consequently weakens the person’s immune system making them susceptible to opportunistic infection and cancer - both of which can be life-threatening.
Where Did HIV Originate?
A debate among the scientific community since the emergence of HIV in the 1980s is the origin of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. The closest strain that is found to be identical to the HIV strain on humans is the Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) which occurs in chimpanzees.
In a study conducted by the Department of Medicine of the University of Alabama, they concluded that the virus has jumped from chimpanzees to humans. The chimpanzees developed SIV when they ate two different species of monkeys carrying different SIV strains.
Currently, there are two types of HIV that have been deeply studied:
- HIV-1 (Group M). This is the type that has been prevalent and has affected almost 75 million people around the world.
- HIV-2. This type is rarer and less infectious than the first type and is usually prevalent in countries located in West Africa.
What Are The Different Causes of HIV?
Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) can be done in specific activities only. Most of these activities involve the exposure or exchange of bodily fluids and the sharing of equipment that causes exposure to the bloodstream. Below are some of the common mode of transmissions of HIV:
- Vaginal, Anal and Oral Sex: Having sexual activity with someone who has HIV and without the usage of condoms may cause exposure to bodily fluids - semen, vaginal and rectal fluid, and pre-cum fluid. The exposure to such fluids may cause the acquisition of HIV, especially if there are no medicines taken to prevent HIV. Specific sexual activities that may cause HIV transmission include:
- Cunnilingus
- In cunnilingus, the outer genital area of the woman (labia, clitoris and vaginal entrance) is stimulated with the mouth. Usually the virus concentration absorbed in this way with the vaginal fluid is not sufficient for infection. Apart from this, the oral mucosa is not very sensitive. In the case of small injuries in the pubic area or in the mouth or during menstruation, however, contact with blood can lead to HIV infection. So-called dental dams can be used to protect against infection. These wafer-thin cloths made of latex or polyurethane are placed over the outer genital area and, like condoms, are available in various variations.
- Fellatio
- A slightly higher risk of infection exists with fellatio, the oral stimulation of the penis. If ejaculation occurs in the oral cavity, the HI virus can be absorbed through the oral mucosa or through small injuries in the oral cavity. However, HIV transmission via fellatio has so far only been documented in isolated cases.
- Sadomasochistic sexual practices
- Since the intact skin offers sufficient protection against HIV, no transmission can occur when stimulating the vagina, penis and anus with the hand. Ejaculation or urinating on the skin is also harmless. Caution is required, however, as soon as blood is involved, or as soon as sexual practices can lead to small injuries that are not visible - for example in the vagina.
- Sex toys
- Dildos, vibrators and other sex toys should always only be used by one person or when used by several people with a condom. It is best to clean them thoroughly with a disinfectant solution before passing them on.
- Sharing of Needles and Syringes: Needles and syringes used to inject drugs or to do a tattoo when shared by one person who has HIV, and one HIV-negative person can cause the transmission of the virus to the HIV-negative person.
- Blood Transfusion: Although it is rare to occur due to blood screening done, a person who has HIV can transmit the virus when he donates his blood to a person without HIV.
What Are The Risk Factors of HIV/AIDS?
Based on the identified modes of transmissions above, these are the people who have increased chances of acquiring HIV/AIDS:
- Sexually Active People. People who are engaged in sexual activities on both men and women and have multiple partners have her chances of getting HIV especially if they don’t use condoms.
- People Who Share Syringes / Needles with other people. As mentioned, any equipment that has been exposed to the bloodstream of a person with HIV can transmit the virus if another person uses the syringe or needle.
- People who receive blood on a regular basis. Albeit rare, it is still possible to acquire blood if infected blood enters your body.
What Are The Risk Factors of HIV/AIDS on Women?
Most of the factors that increase the risk of women acquiring HIV/AIDS are the same as men however below are the most common risk factors:
- The most common way for women to acquire HIV is by having vaginal sex with men without a condom.
- Women who engage in vaginal sex and do not use condoms have a higher risk of being passed with HIV if their partner is HIV-positive.
- If a woman also has a partner that is engaged in multiple sexual activities, then the risk of getting HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases.
What Are The Risk Factors of HIV/AIDS on Men?
Generally, men also have the same risk factors as women, especially if they are engaging in sexual activities. However, men have a higher risk of getting HIV if they have:
- Anal Sex With Men. According to this study, men who have anal sex with men using lubricants or condoms have a higher risk of getting HIV.
- Multiple Men Partner. Additionally, men who have multiple partners add a risk factor as any of their partners may be HIV-positive.
How can HIV infections progress?
An HIV infection can be divided into three phases.
Phase 1: Acute HIV disease and latency phase
When the HIV virus enters the body, it triggers a defensive reaction. However, the immune substances (antibodies) formed in the process are not able to eliminate the virus because, on the one hand, they cannot penetrate the host cell and, on the other hand, the virus constantly changes its surface structure as it multiplies, so that it no longer recognises the antibodies. Thus, the HI virus remains in the body for life.
After infection, the pathogen initially multiplies explosively. This early phase of the disease often goes unnoticed by those affected. In 40-90 percent of cases, the so-called acute HIV disease develops a few days to weeks after infection.
The most common symptoms are:
- Fever
- Headaches
- Joint pain
- Fatigue & exhaustion
- Swelling of the lymph nodes
- Loss of appetite
- Inflammations in the mouth & throat
- Diarrhoea
- Sometimes a fleeting skin rash
After about two weeks these complaints disappear again. At the end of this phase, the number of T-helper cells has recovered and the amount of virus in the blood has decreased considerably.
This is followed by the latency phase. Without therapeutic intervention, it lasts on average about ten years. In this phase, those affected are free of HIV-related symptoms because the body's own defence system can keep the virus under control to a large extent. Nevertheless, the immune system has to deal with the HI viruses on a daily basis and at some point, it loses this battle: the viral load increases and the number of T-helper cells decreases.
Phase 2: Symptomatic phase
This increasing weakening of the immune system heralds the symptomatic phase. First, the dwindling ability of the immune system to function becomes apparent in the form of complaints such as night sweats, fever attacks and diarrhea. Many of those affected also suffer from fungal infections of the mucous membranes (e.g., oral cavity), other skin symptoms (e.g., shingles) and swelling of the lymph nodes.
Phase 3: AIDS
If the immune system is further weakened, it is no longer able to defend itself against pathogens that do not pose any danger to healthy people. Then the affected persons develop so-called AIDS-defining diseases. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome" is a defined group of diseases that are characteristic of an advanced stage of HIV infection.
These include pneumocystis pneumonia (a form of pneumonia), fungal diseases or infections with viruses such as herpes zoster or herpes simplex. Cancer diseases are also favoured by immunodeficiency.
In addition, HIV also damages the brain and nervous system, which leads to brain performance disorders that begin slowly and inconspicuously. Once the full picture of AIDS has been reached, those affected die sooner or later without therapy from one or a combination of these diseases.
Complications of HIV/AIDS: Categories, Examples, and Treatment
With HIV being an immune system-damaging disease, there are many complications in your health and lifestyle that come along with it. These complications can be life-threatening and can interfere with daily life depending on the severity or nature of the complication. Below are some of the common questions and its respective answers with regards to complications of having HIV and AIDS:
What Are The Possible Complications of HIV?
There are many possible complications that an HIV-positive person may encounter because of their weak immune system. Below is a categorized list of these complications:
Common Infections
These are common infections that may affect even those people who are not diagnosed with HIV. Most of these infections can be treated with proper medication if diagnosed early.
- Cryptosporidiosis. This disease is similar to diarrhea but in a chronic manner accompanied by severe abdominal cramps.
- Histoplasmosis. A type of fungal infection that affects the lungs by inhaling Histoplasma capsulatum fungal spores. This can be treated with antibiotics.
- Coccidioidomycosis. Commonly known as valley fever, this is caused by the fungus Coccidioides and it affects the lungs of a person, this can be treated with antibiotics.
Opportunistic Infections
Opportunistic Infections are classified as infections that have severe effects on people who have weak immune systems - this includes people who are diagnosed with HIV. Due to the weak immune system, the body is having a difficult time fighting off HIV-related opportunistic infections and consequently, they can be life-threatening. Below is a list of some of the opportunistic infections observed in HIV-positive population:
- Candidiasis. Also known as thrush, this is typically a yeast infection that occurs in the mouth. It can be treated with antifungal treatment but can be lethal if left untreated
- Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia (PCP). A form of pneumonia caused by a yeast-like fungus and is the leading cause of death amongst HIV-positive people. Being a fungal infection can be treated using proper antibiotic therapy.
- Salmonella Infection. An infection caused by the Salmonella bacteria and affects the intestine, this can lead to death if left untreated on a person with HIV. This can be treated using antibiotics.
- Herpes Simplex Virus. People who are diagnosed with HIV are more prone to sexually transmitted infections such as Herpes which manifests by producing ulcers in the mouth and genital areas. These can be treated also with antibiotics as long as it is diagnosed as early as possible and the HIV-positive person has been taking regular medicines to suppress HIV.
Other opportunistic infections associated with HIV/AIDS Infections include:
- Opportunistic infections of the lungs such as coccidioidomycosis, acquired by the inhalation of fungal spores and cryptococcosis caused by infection with the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. The latter can spread other body parts including the brain where it causes swelling (cerebral edema).
- Chronic diarrhea lasting more than one month due to cryptosporidium infection, isosporiasis or salmonellosis.
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis affecting the eyes.
- HIV encephalopathy affecting the brain and altering its function.
- Tuberculosis, a chronic lung infection caused by the bacteria mycobacterium tuberculosis which also in some cases affect other body parts such as the bones, kidneys, brain, or lymph nodes. Recurrent pneumonia, lung infection caused commonly by streptococcus pneumoniae.
HIV wasting syndrome which is defined as the unintentional weight loss of more than 10% of total body weight in the presence of chronic diarrhea, fever, and weakness for 30 days or more.
Cancers
- Lymphoma. Known as cancer of the lymph nodes, people with HIV have a higher risk of acquiring lymphoma as lymph nodes help in fighting infections and bacterias within the body. Since this type of cancer comes in various forms, treatment is dependent on the condition and type in addition to HIV treatment.
- Kaposi’s Sarcoma. A cancerous tumor that appears in multiple locations on the skin and different areas such as nose, mouth, genitals, and anus. There are lesions that may appear in these various areas of the body. Treatment for this cancer is chemotherapy and radiation in addition to antiretroviral therapy for combating HIV.
What Are The Possible Complications of AIDS?
Since AIDS is already the final and advanced stage of HIV, there are more severe complications that come with it. Some of this include:
- Tuberculosis. A contagious disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis; this disease is also one of the leading causes of death of people with HIV. The symptoms for this infection are usually a chronic cough which includes blood. It is highly recommended to be screened for TB once a person is diagnosed with HIV. In most cases, Tuberculosis is considered as a condition that confirms that HIV has progressed into AIDS.
- Toxoplasmosis. A parasitic infection that targets people who have very low CD4 cell counts - this includes people who are already in the AIDS stage.
- HIV-related encephalopathy. Similar to dementia, this is a degenerative brain condition that affects people with CD4 counts below 100 per cubic millimeter.
Are There Any Specific Complications For Men?
There are no major specific complications for men, however, all complications above may occur to men who are diagnosed with HIV.
Are There Any Specific Complications For Women?
- Vaginal Infections. Although vaginal infections such as yeast infections and bacterial vaginosis are common to women, women who are HIV-positive are at a higher risk of having repeated vaginal infections due to their weakened immune system.
- Cervical Cancer. This type of cancer that occurs in women is very common to women who have HIV, especially if they are already in an advanced stage already.
- HIV Transmission to Child. Bodily fluids are shared from a mother to child so if a woman with HIV gets pregnant, there is a high chance that HIV may be transmitted to a child. Another mode of transmission from a woman to a child is through breastfeeding. If diagnosed early, these types of complications can be managed to avoid transmission of HIV to the baby.
How is HIV infection diagnosed?
HIV is diagnosed by a specific blood test or mouth swabs. These tests look for specific antigens and antibodies which indicate the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus. Note that the emergence of these antibodies only within 23 to 90 days after contracting HIV.
The Ultimate Guide To Treatment of HIV/AIDS
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) cannot be eradicated once it enters a person’s body. However, there are many scientifically proven effective ways on how to treat and manage it in order to have a comfortable and productive life. Depending on the condition and progression of HIV, there are various options on how to manage it. Here are some questions and answers about the treatment options of HIV and AIDS:
What Are The Treatment Options for HIV?
Post-exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
This is considered an emergency HIV drug that is to be taken within 24 to 72 hours of being exposed to the virus. This is no different from antiretroviral drugs (ART) but this treatment means the consumption of ART after being suspected to be exposed from HIV.
How would you know if you have been potentially exposed to HIV?
- If you’ve engaged in sexual activity with an HIV-positive person without the usage of condoms or if there was breakage of condoms.
- You’ve shared needles or syringes with someone who is HIV-positive.
- Received a blood transfusion or your bodily fluids of someone who is HIV-positive has been transferred to you via an open wound - this is rare but possible.
Where Is PEP available?
PEP requires a prescription from a doctor but any healthcare provider can give it to you as long as you have sufficient information about your potential exposure to HIV
What Are The Side Effects?
There are no life-threatening and severe side effects of PEP but may cause nausea to some people.
What is the usual course when prescribed with PEP?
Usually, most people take PEP once or twice for a span of 28 days. This is not an ideal medicine for people who are frequently exposed to HIV (e.g. having a partner who is HIV-positive). The PEP should also be used for emergency purposes only.
Antiretroviral Drugs (ART)
Antiretroviral drugs or therapy work by suppressing the virus, its progression and its effect on the body. While this type of drug does not completely eradicate the virus from the body of an HIV-positive person, it helps decrease the risk of complications and improves the quality of life. The purpose of the drugs is to reduce the viral load of a person to undetectable levels, so if an HIV-positive person who has been taking ART for a period time subjects himself to HIV-test, there is a chance that he might be diagnosed as HIV-negative - but this does not mean that HIV is no longer existent in his body, it simply means that the viral load of HIV is so low that it is no longer detectable.
How does ART work?
It prevents HIV from spreading and multiplying over a person’s body so the person’s healthy cells, which include CD4 cells are protected instead of being targeted by the virus. Treatment from HIV may require a combination of different types of antiretroviral drugs and there are already medicines that contain combined classes of these drugs. If treatment is effective, it is expected that the viral load within an HIV-positive person will decrease within 6 months.
What are the different types of ART?
There are many different types of ART and each of them differs based on the type of enzyme or the site of the enzyme that they act on. See below for these categories:
Category | How It Works | Enzyme Acted On | Example Drugs |
Entry Inhibitors | Prevents HIV from entering targeted cells (CD4) | Enfuvirtide Maraviroc | |
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) | Blocks viral reverse transcriptase - an enzyme required to replicate HIV | Viral Reverse Transcriptase | Delavirdine Etravirine Nevirapine Rilpivirine Doravirine |
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) | Blocks viral reverse transcriptase - an enzyme required to replicate HIV | Viral Reverse Transcriptase (different site) | Abacavir Emtricitabine Stavudine Tenofovir Lamivudine |
Integrase Inhibitors | Blocks the transmission of genetic material from HIV to CD4 cells | Integrase | Raltegravir Elvitegravir |
Protease Inhibitors | Impedes HIV protease which is required to replicate HIV | HIV Protease | Atazanavir Fosamprenavir Lopinavir Ritonavir |
The following outline further describes the specific mechanism through which each of these antiretroviral medications deliver its desired action:
Entry and Fusion Inhibitors (EIs) – Drugs of this class keep the HIV from fusing, binding and getting into the T cells. EIs are used along with other HIV drugs.
Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs) – The drugs of this class block integrase, which is an enzyme HIV must have to replicate. HIV will use integrase to add its viral DNA to the T cells DNA. Blocking the process means HIV cannot replicate. They are taken in conjunction with other HIV meds.
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) – Drugs here will block reverse transcriptase, which is the enzyme HIV must have to replicate. The virus will use the reverse transcriptase to change the RNA it has into DNA, which stops the process and the HIV from reproducing. These drugs are taken with other HIV drugs.
Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) – These drugs stop reverse transcriptase just like NRTIs but in another way. They are used simultaneously with their drugs.
Pharmacokinetic Enhancer/CYP3A Inhibitors (PKE) – These drugs increase the effectiveness of the antiretroviral medication. When two of them are taken simultaneously, the PKE slows the other drug’s breakdown, ensuring the drug to stay in the body longer at a higher level. These are used with other HIV drugs.
Post-Attachment Inhibitors (PAIs) – These drugs will bind to CD4 cells after the HIV attaches to them, but keep the HIV from getting into the cells. They are used with other HIV meds.
Protease Inhibitors (PIs) – The drugs in HIV class block protease activation, which is the enzyme HIV must have to grow. By blocking the protease, it stops the premature types of HIV from growing into a mature virus that can infect the T cells. These are used with other medication for HIV.
Single-Tablet Regimens (STRs) – These fixed-dose pills combine several anti-HIV meds into one tablet and are taken one time a day. These meds are not used with any HIV medication.
How Is Treatment Monitored?
Treatment is monitored by periodic monitoring of CD4 cells and viral load.
For patients that have a higher risk due to age or condition, kidney and liver function tests are done.
Are There Side-Effects For The Treatments?
Depending on the condition of the person, there are various side effects that can happen once HIV medicines are taken in a regular manner. Below are some of the most common side effects:
- High blood sugar and diabetes
- Kidney Damage
- Liver Damage
- Bone Loss
- Nauseousness
- Vomiting
- Lack of sleep
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Headaches
- Rash
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Pain
If another medication for another illness is to be done, one must consult her GP to ensure that there are no harmful interactions to your HIV medicine.
What Is AIDS and How Is It Related to HIV?
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, or simply known as AIDS is a syndrome that can develop in people who have human immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV). The nature of HIV is to kill CD4 cells - the same cells that are part of the immune system and fights infections. The normal quantity of CD4 cells in a healthy person ranges from 500 to 1500 per cubic millimeter, if a person has a count of less than 200 per cubic millimeter - they are diagnosed with AIDS. Usually the progression from HIV to AIDs averages in about ten years. A person can only acquire AIDS if they have HIV but not all those who have HIV can have AIDS. People who are diagnosed with HIV at an early stage and managed properly have lower chances of getting AIDS.
What Are The Treatment Options for AIDS?
AIDS is an advanced stage of HIV has no cure. For people diagnosed with AIDS, they have the same treatment options as those who have HIV-1 or have a combination of different antiretroviral drugs and medication for their complications. Their treatment is based on the severity of their complications and how much the virus has spread throughout their body.
10 Essential Methods of Prevention and Spread of HIV/AIDS
With Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) becoming rampant and prevalent around the world, different health institutions and organizations have developed and disseminated various information on how to prevent spread and acquisition of HIV. We’ve listed down a list of informative prevention methods below:
General Methods of Prevention of Acquisition of HIV
Abstinence
Avoidance of any sexual activities is the most effective (100%) method of preventing HIV. If you think you’re at risk of having HIV or by personal choice you want to wait before being sexually committed - abstinence will surely prevent a person from getting HIV. The most common mode of transmission of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (e.g. chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea) is through sexual activity so being abstinent will surely prevent any person from acquiring such diseases.
Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
If you have engaged in any activity - sexual activity or sharing of medical paraphernalia that might have exposed you to the virus, you can reach out to the nearest medical facility, ideally between 24-72 hours, to stop being fully infected by HIV. This medication is en emergency HIV medicine that if administered correctly can prevent a person from being infected with HIV.
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
This is a prevention strategy aimed at individuals who are at high risk of acquiring HIV. This method requires administering medicine to be taken daily. This preventive approach is recommended to people who are at high risk of acquiring HIV such as those who are:
- Having sexual activities especially anal and vaginal sex
- Having sexual activities without using condoms
- Having sexual activities with a partner who is HIV-positive or has multiple partners
- Sharing medical equipment with someone who is HIV-positive
Avoid Sharing of Needles/Syringe
Stop sharing equipment (e.g. needles and syringes) with other people - especially if you live with an HIV-positive person to conduct medical procedures that require the usage of any equipment that is exposed to bodily fluids. If any of these procedures are done in a public or shared facility - make sure that the needles and syringes are new and sterile.
Blood Screening If You’re a Blood Recipient
Although it happens rarely; if you are going to receive blood donation or any blood component. Most hospitals do screening on this but make sure to get firsthand information and confirmation that your donor has been screened properly for any blood-transmitted diseases.
Limit Your Number of Sexual Partners/Activity
If abstinence and usage of condoms are not feasible, then move to limit your sexual activities or sexual partners. Studies show that
- There is a higher risk of acquiring HIV through vaginal sex and anal sex versus oral sex.
- Women have a higher risk of acquiring HIV from men during vaginal sex than men acquiring HIV from women.
- Men have a higher chance of acquiring HIV if they engage in anal sex with men.
- Having a monogamous sexual relationship - especially if you are both HIV-negative decreases the risk of getting HIV significantly.
Methods of Prevention of Spread of HIV
Practicing Safe Sex
Usage of latex condoms, female condoms, and dental dams during sexual activities decreases the risk of spreading HIV and ensures that your partner is protected if you are HIV-positive. Condoms help in preventing your partner from being exposed to your own bodily fluids (e.g. semen and pre-cum).
Generally, most condoms are made of latex and polyurethane. The latter is suitable for those who have latex sensitivity or allergies. It is also what female condoms are made of.
Although this is not a 100% effective method as condoms may have breakage, this is a good practice to be followed as this also avoids transmission of other sexually transmitted diseases. This prevention method is also applicable in the prevention of acquisition of HIV.
Antiretroviral Drugs/Therapy (ART)
If you are diagnosed as HIV-positive, treatment should start right away to prevent further damage of the virus to your immune system. The treatment should decrease the viral load in your body up to a low level of viral load wherein you are less likely to transmit HIV to another person. Taking and following proper HIV treatment such as ART helps not only the person with HIV but their sexual partners and their community as well.
Regular Screening
Once diagnosed with HIV and you have undergone treatment if done properly, your viral load becomes so low that it becomes undetectable (but not gone from your body). Having HIV becoming undetectable indicates that your treatment is working and to monitor this you have to have regular screening of your viral load and CD4 count as well as check for the presence of antibodies for HIV in your blood. Regular screening not only serves as monitoring for your condition but also helps reassure your partner that they have a lower chance of being infected.
Engage in Less Risky Behaviors
Having HIV changes people and this includes their behaviors or response to sexual activities. If you are HIV-positive, avoid activities that might expose people from the virus within your body. This can be done by:
- Commit to treatment and monitor your status regularly.
- Abstain from sex if possible.
- For women, use condoms with men who are HIV positive.
- For men, avoid engaging in anal sex with other men.
Invest In Building A Relationship with Your General Physician or Doctor
HIV is a lifelong condition that will need to be dealt with always so it is important to have a solid relationship with your general physician - the doctor will have the best medical opinion as to what is the best option for you to handle your condition. Your general physician will also assess and warn you for any activities that will endanger or complicate your condition if you engage in any activities.
Things to Note in Cases of Accidental Contact with Bodily Fluids During Sexual Intercourse
- If an unwanted ejaculation occurs in the mouth, spit out the sperm as quickly as possible and rinse the mouth with a disinfectant solution or alcohol.
- However, you should refrain from rinsing if a condom bursts in the vagina or an unwanted ejaculation occurs in the vagina. Flushing only transports the viruses further into the vagina. By the way, there are also HI viruses in the lust droplet - albeit in lower concentrations. The lust droplet is a clear liquid that enters the urethra before ejaculation and is secreted shortly before ejaculation.
- If blood, semen or vaginal fluid has reached a wound, the wound should be rinsed well with water and disinfected for several minutes.
- If a risk contact has occurred, post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is a medicinal measure that can often be used to avert an HIV infection. It is important that PEP is administered as quickly as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About HIV/AIDS
With Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) being one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases, there is a truckload of information and studies available on the internet and most of them contain detailed information about every sector of the nature of the virus.
We’ve compiled a list of the commonly asked questions below:
1. What are the top 3 risks for acquiring HIV?
- Having sexual activity with someone who is HIV-positive without the use of condoms
- Sharing needle and syringe with someone who is HIV-positive
- Having multiple sexual partners
2. How accurate are HIV tests?
Tests have up to 99.83% accuracy if they are done in the proper time window and with an uncontaminated specimen.
3. What is the life expectancy of someone who has HIV?
If you have HIV and have undergone treatment early or before AIDS, your life expectancy can be as long as a normal and healthy person. The earlier you are diagnosed, the higher the life expectancy there is.
4. What is the life expectancy of someone who has AIDS?
Having a full-blown AIDS limits a person’s life expectancy from 3 months up to 6 years depending on the complications encountered.
5. How will HIV affect my child If I get pregnant?
If a woman who is HIV-positive gets pregnant, then there is a chance that they may pass the virus to their child. To avoid this, the woman should take ART immediately as possible and discuss other treatment options that can decrease the risk of transmission of HIV with their ob gyne.
6. Can I still engage in sexual activities even if I am diagnosed with HIV?
Yes. However, your partner should be aware of your condition and you should protect him or her from acquiring HIV from you by taking treatment or by using condoms.
7. When should I seek for an HIV Test?
If you think you have HIV because you have multiple partners or your partner is HIV-positive, you should ask for HIV screening the soonest time possible.
8. How long does HIV progress to AIDS?
This is dependent on some factors like whether or not the individual is on antiretroviral therapy and their general health background but on the average, it takes about 10 to 15 years to progress to AIDS. It could be longer or shorter. Regular treatment with antiretroviral drugs can reduce HIV viral load to undetectable levels which prevent the progression to AIDS.
9. What should I expect if I have HIV/AIDS?
- Living with HIV is a significant change in your life - there is no treatment for it but it can be managed effectively if you are committed with your treatment.
- Living with AIDS is difficult because there are periods that your health may suffer severely due to complications - if your HIV has progressed to this stage, it is better to discuss with your doctor as to what is the best way to handle your case so that your quality of life will improve.
10. Are there any foods to be avoided if diagnosed with HIV?
- To avoid any complications, people with HIV are encouraged to eat healthy foods (e.g. vegetables, lean protein, and low sugar foods) like other people.
- There is no specific food that needs to be avoided.
11. How frequently should I visit the doctor if I have HIV?
- Since HIV is a lifelong condition, monthly regular checkups, screening, and treatment assessment is recommended.
- This aids in assessing if your treatment is working accordingly or if there any treatment changes or tests that need to be done.
12. Can HIV be transmitted through other modes other than bodily fluids?
No. HIV can only be transmitted through bodily fluids. Below are some of the misconceptions that will not be able to transmit HIV from one person to another:
- Sharing clothes, utensils or bedrooms
- Saliva
- Air particles
13. Is there any chance that I can be cured with HIV or AIDS?
As of now, there is no cure for HIV/AIDS. Clinical trials for cure and vaccine are ongoing but those who are diagnosed with HIV can undergo the effective treatments that are available and they can have the same life expectancy as other people.
14. How does age affect the possibility of acquiring HIV?
HIV is common in sexually active people aged 13-24. However, you can get AIDS at any age as long as you are exposed to the virus.
15. How does smoking increase the risk of HIV?
Smoking does not increase the chance of acquiring HIV. However, if you are already HIV-positive and you are a smoker, there is a risk for you to get complications that can turn to opportunistic infection and can be life-threatening.
16. I’ve been diagnosed with HIV and I have undergone treatment. My latest HIV screening says that there is no virus detected in my body. What does this mean?
If you have already undergone treatment and your latest HIV screening indicated that there is no viral load in your body - this does not mean that you are HIV negative. It only means that the treatment is working and has brought the virus to undetectable levels.
17. What happens if I miss my treatment or discontinue my treatment?
- If you miss your treatment, there is a chance that the virus may act and try to kill CD4 cells in your body. This can cause damage to your immune system and the severity will likely depend on the amount of dosage you’ve missed.
- If you discontinue treatment, the virus will likely target your healthy CD4 cells and your HIV will continue to progress.
18. Can you stop taking HIV treatment?
No. HIV is a lifelong condition and medication should be taken as long as advised by your doctor. If you stop taking the medicine, the viral load of HIV will likely increase and damage your immune system.
19. What are the top three countries with the highest HIV-positive population?
The top 3 countries with the highest HIV prevalence are as follows:
- South Africa
- Nigeria
- India
20. Is there a population that is HIV-resistant?
According to this, people with CCR5 mutations have innate resistance against HIV. CCR5 is the co-receptor of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Less than 1% of people are projected to have this kind of resistance.
21. What does the term safer sex mean?
As they say, the only safe sex is no sex at all, i.e. abstinence. But safer sex involves precautions, methods, or devices employed during sexual activity to greatly lower the chances of HIV transmission, as well as the timely treatment of other sexually transmitted infections.
Safer sex still carries some risk but is much lower than otherwise. These precautions include:
- Consistent and proper use of protection (male and female condoms) during sex.
- Have only one sexual partner who also is having sex with you alone.
- Oral sex and non penetrative sex are considered safer sex and can be made even more so by the use of dental dams and condoms.
- Take pre-exposure prophylaxis if you are at risk of HIV infection.
- Take antiretroviral drugs consistently if you are HIV-positive in order to achieve an undetectable viral load.
22. Are condoms truly effective in the prevention of HIV transmission?
If you consistently and properly use condoms, they are highly effective in protecting against HIV transmission. They equally protect against other sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea. However for sexually transmitted infections which are spread via skin to skin contact such as genital herpes, genital warts, and syphilis, they are less protective.
Even though they are highly effective, there's still a chance of HIV transmission so it is recommended that you add other methods of prevention to further reduce the risk.
23. How do I make the best choice of condoms to use?
Generally, most condoms are made of latex and polyurethane. The latter is suitable for those who have latex sensitivity or allergies. It is also what female condoms are made of.
These materials have been shown to effectively prevent the passage of hepatitis, herpes virus, and of course the HIV virus. Condoms made of natural substances (lambskin) are not able to do this.
There are some condoms designed for sexual stimulation and not protection against sexually transmitted disease. These typically do not say anything about disease prevention on the package. Also condoms should be of appropriate length, covering the entire penis.
24. Is it okay to use lubricant together with a condom?
For condoms that are not already lubricated, you may apply some lubricant yourself. Some of them however are already lubricated using jellies, creams, and silicone.
Using a lubricant helps to prevent irritation or breakage while in use. Water-based lubricants are recommended.
Avoid oil based or petroleum based ones as they can cause damage to the latex material, making them prone to micro tears.
25. What is post exposure prophylactic treatment?
Post-exposure prophylaxis is a short-term course of HIV drugs which is taken just after an individual has been potentially exposed to the virus.
It is used only in cases of emergencies and not on a regular basis when exposure is continuous or frequent.
It consists of antiretroviral medication which is highly effective in HIV prevention if taken properly. It should ideally be taken not later than 72 hours post exposure.
26. In what ways can injecting drug users lower their risk of getting HIV?
To reduce your risk of HIV infection, as an injection drug user you can do the following:
- Switch from injection drugs and go to oral vacation medication.
- Each time you want to prepare your drugs, make sure it's with new syringes. Don't share your syringes or use them more than once.
- Use water from a trusted source to mix your drugs.
- Ensure you swab the intended injection site with an alcohol wipe or swab.
27. Can mother to child transmission (MTCT) be prevented? How?
Mother to child transmission otherwise known as a vertical transmission is responsible for a good majority of cases of HIV infection in children aged 0 to 14 years.
This transmission can occur during pregnancy, childbirth, or via breastfeeding. For an infected mother who is left untreated, the chances of infecting the baby is about 15 to 30%. Breastfeeding also increases the chances considerably. With treatment, it comes down low to 5%.
As a means of curbing this, the World Health Organization has recommended a program which offers care to HIV positive women from the time of pregnancy through delivery to breastfeeding.
These services include:
- Early infant diagnosis at 4-6 weeks after birth with HIV testing at 18 months and/or commencement of breastfeeding.
- They are to be started on antiretroviral therapy as early as possible if there has been HIV exposure.
- Infected mothers are also to be compliant with their antiretroviral medication.
28. What are universal precautions?
Universal precautions are a set of guidelines which healthcare workers are expected to follow in order to limit the spread of infection from blood and other body fluids, and thus protect their health and that of the patients in their care.
These precautions include:
- Washing your hands carefully and often with soap and water.
- Use protective barriers like gloves, gowns or aprons and masks when direct contact with blood and other body fluids is expected.
- Safe collection and disposal of needles and "sharps" (boxes for safe disposal are needed for this).
- Follow the right procedures when a needle–stick injury occurs. Wash the area properly with soap and water and dispose of the needle safely (to avoid getting injured a second time), go to the Accident and Emergency immediately so as to be assessed for post exposure prophylaxis).
- Cover all cuts and abrasions with dressings that are waterproof.
- Clean up blood spills and other body fluids with bleach and water solution in the ratio of 1:10.
- Use a different mop for body fluid spillages and meticulously dispose of every equipment used in the clean up of the spillage.
29. What is the mechanism of action of antiretroviral drugs?
Numerous drugs are now available for HIV therapy. Most of them work by blocking the activity of enzymes (proteins that accelerate and facilitate chemical reactions) specific to HIV and necessary for it to multiply in its target cells. These cells are represented by a subgroup of white blood cells, called CD4+ lymphocytes (ie lymphocytes that express a molecule called CD4 on their surface), which are a part of the immune system and are essential for adequate defense against infections. The HIV enzymes blocked by these drugs are integrase, reverse transcriptase and protease.
30. Are antiretroviral drugs efficacious?
Antiretroviral therapy is able to effectively suppress the quantity (viral load) of the virus in the blood, reducing them almost to undetectable levels, to eliminate the risk of transmission of HIV among sexual partners and the risk of transmission from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth (vertical transmission of HIV).
For antiretroviral therapy to be effective, it is therefore necessary to ensure that HIV is no longer detectable in the blood. This goal can only be achieved if antiretrovirals from different classes are combined.
Otherwise, HIV continues to be present in the blood, to multiply and weaken the immune defenses, and in a short time, it inevitably becomes resistant to the drugs used, making them ineffective.
It is possible to identify the presence of drug-resistant viruses with specific tests, and in these cases, the drugs against which resistance has been identified are replaced with drugs to which sensitivity has been maintained, usually of different classes.
In any case, antiretroviral drugs are not able to eliminate HIV from the body because HIV remains permanently present in already infected cells. Therapy therefore aims to stop the multiplication of the virus in a lasting way.
Once started, the therapy must be followed indefinitely and cannot be interrupted or taken in a discontinuous way.
There are currently no drugs with prolonged time of action to be taken once a week or a month, and it is therefore necessary to take antiretroviral therapy every day respecting the indicated doses and times.
However, very simple combinations are now available, in which it is possible to take all the therapy provided in a single administration a day, sometimes represented by a single tablet to be taken in the evening.
- HIVinfo.NIH.gov. (2019). HIV/AIDS: The Basics. Retrieved August 2021
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). HIV Basics. Retrieved August 2021
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). About HIV. Retrieved August 2021
- HIV.gov. (n.d.). HIV Basics. Retrieved August 2021
- Alameda County Public Health Department. (n.d.). Basic Information About HIV/AIDS. Retrieved August 2021
- Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology. (n.d.). The Very Basics About HIV and AIDS. Retrieved August 2021
- Avert. (2020). What are HIV and AIDS? Retrieved August 2021
- Avert. (2018). The Science of HIV and AIDS. Retrieved August 2021
- KidsHealth. (2018). HIV and AIDS. Retrieved August 2021
- amfAR. (2021). Basic Facts About HIV/AIDS. Retrieved August 2021
Written by Mark Riegel, MD
Quick Snapshot
Can it be cured?
No. Viruses don't have cures, but symptoms can be controlled with proper treatment.
Type of Infection
Viral. AIDS is caused by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
How is it treated?
Antiviral Medication. HIV/AIDS is treated with a variety of antiviral medications: fusion inhibitors, protease inhibitors and RT inhibitors are the most common.
Recovery Time
AIDS / HIV is Incurable. HIV/AIDS is incurable; as such treatment is aimed at slowing progression and treating symptoms.
Can I have sex?
Yes. Partners should be informed of your condition and condoms/dams should be used consistently.
Can I get re-infected?
No. HIV is incurable; once you are infected, you will carry the disease with your for life.
Do I Have HIV?
Find out whether or not you have HIV / AIDS and what STD test is recommended using our anonymous symptom checker. Get personalized results and recommendations.
HIV/AIDS Symptom CheckerConcerned about an STD?
Help stop the spread of STDs by knowing your status. Get tested today!